June SonoProps
Summer is in the air, and another edition of SonoProps is out!
This month’s first SonoProps goes to Dr. Stephen Simon.
Dr. Simon had a 30-year-old patient that had felt pop while playing basketball and started having worsening posterior left ankle pain. Radiology interpreted the patient’s X-rays as no evidence of an acute bony fracture in the left foot, ankle, and tibia/fibula with mild soft tissue swelling surrounding the distal left fifth metatarsal.
Dr. Simon grabbed the ultrasound and performed this POCUS:
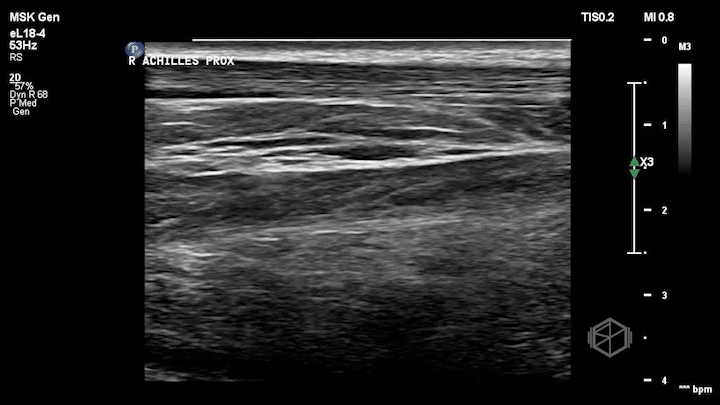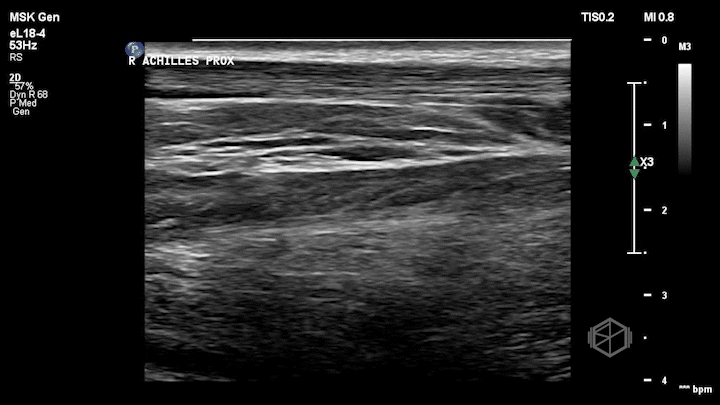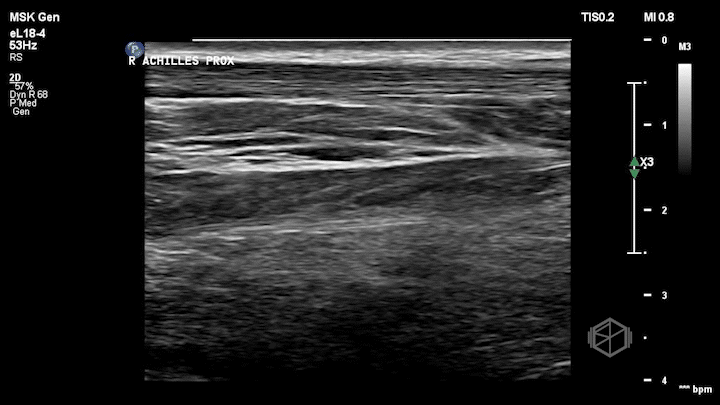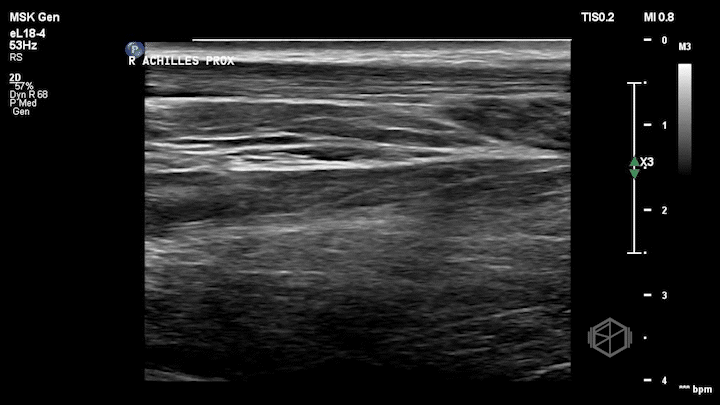
Notice how the right (non-affected) Achilles tendon is nice and smooth. It is the first structure from top to bottom and appears as a thin fibrillar structure.
The left (affected tendon) is irregular with a quite obvious visible tear with some surrounding edema (anechoic fluid).
Dr. Simon included the unaffected tendon for comparison which is a great thing to do when performing with extremity ultrasounds.
Diagnosis: Left Achilles tendon rupture
Learning points:
Ultrasound is an excellent modality for diagnosing tendon injuries, especially the Achilles tendon, with a high accuracy.
Sonography of the Achilles tendon is performed using a high frequency linear probe.
Start from the insertion of the Achilles tendon into the calcaneus in a long orientation and scan proximally past the affected portion. A short view should also be obtained.
A dynamic Thompson’s test can be performed with the ultrasound. Squeeze the calf and visualize the the ruptured portion of the Achille’s tendon for separation.
Obtain clips of the unaffected extremity for comparison.
Aside from visualizing the rupture itself, secondary signs include hypoechogenic areas within or deep to the tendon. A thickened tendon, posterior shadowing, and tendon retraction correlate with full thickness tears.
Power doppler may demonstrate hyperemia indicating neovascularization and subacute injury. A normal tendon should not have any vascularity.
The second SonoProps goes to Dr. Edward Mintz.
Dr. Mintz had a 79-year-old patient that presented with shortness of breath for 2 weeks. The patient had a remote history of malignancy, but no other history. Given the progressive shortness of breath, Dr. Mintz took the ultrasound and performed this echo immediately after seeing the patient:
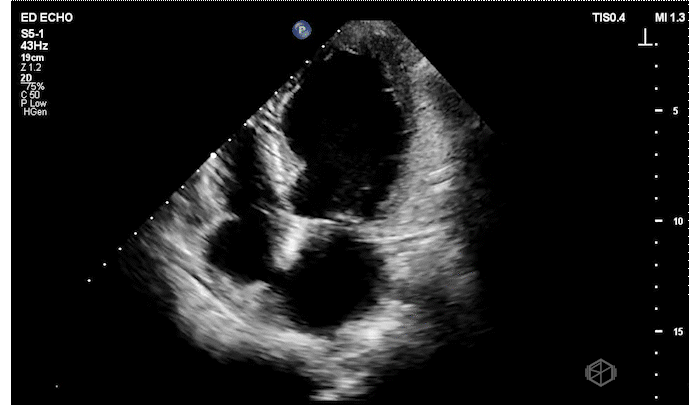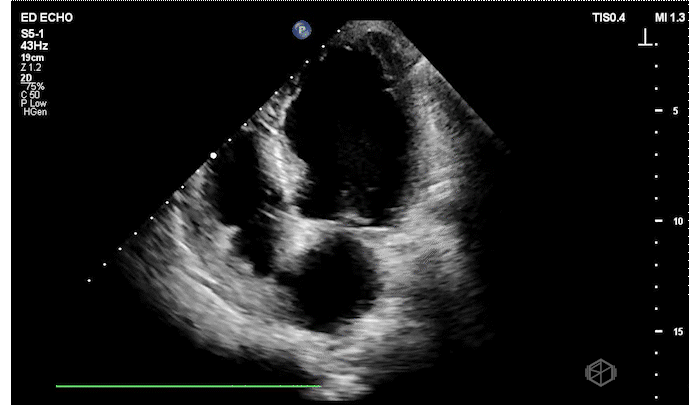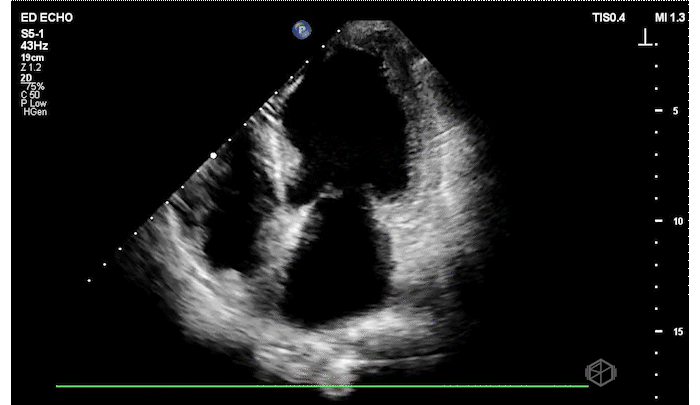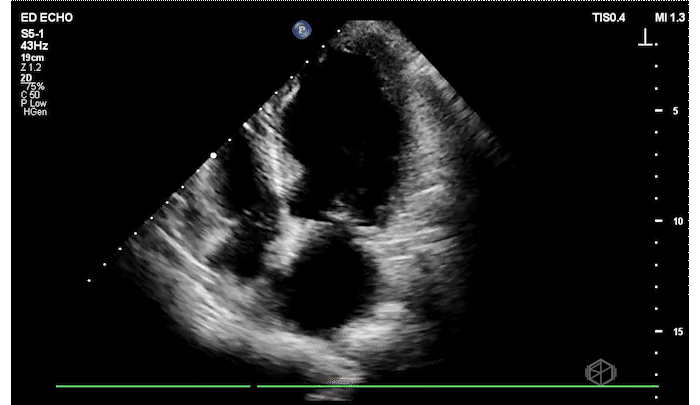
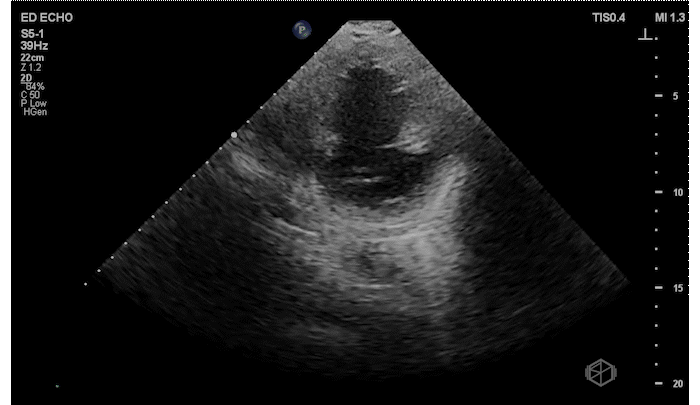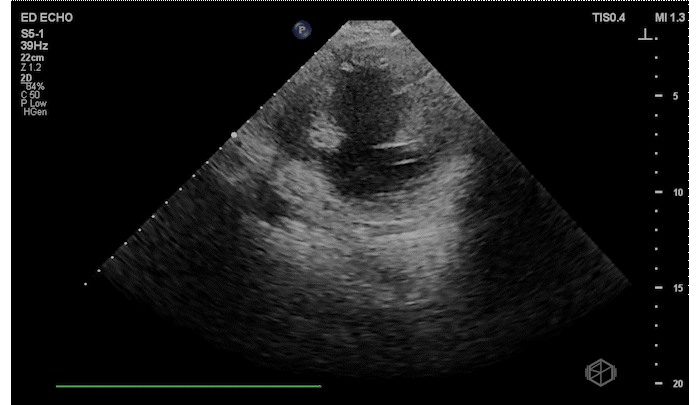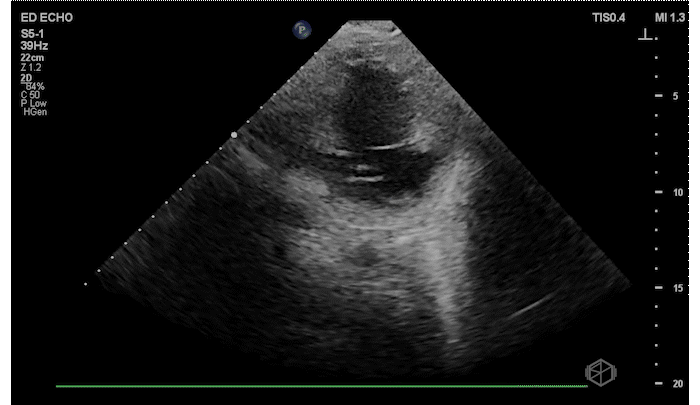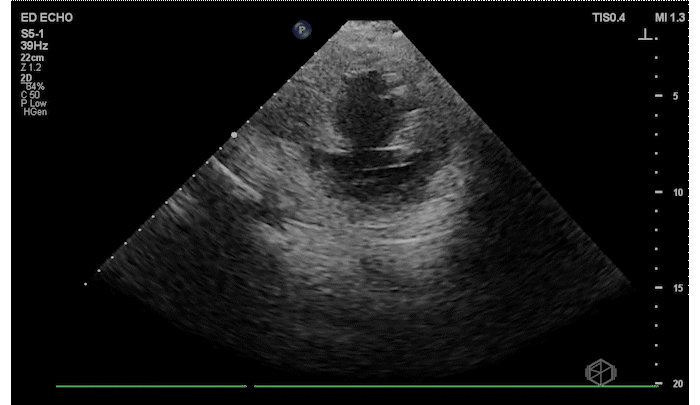
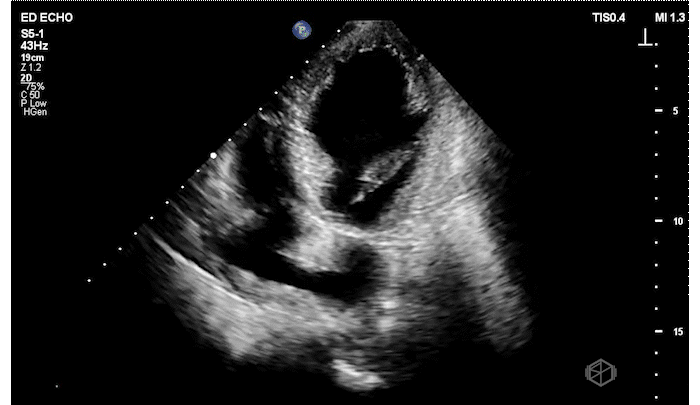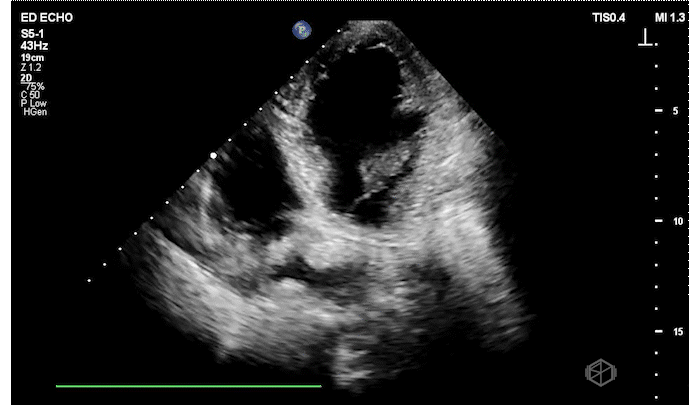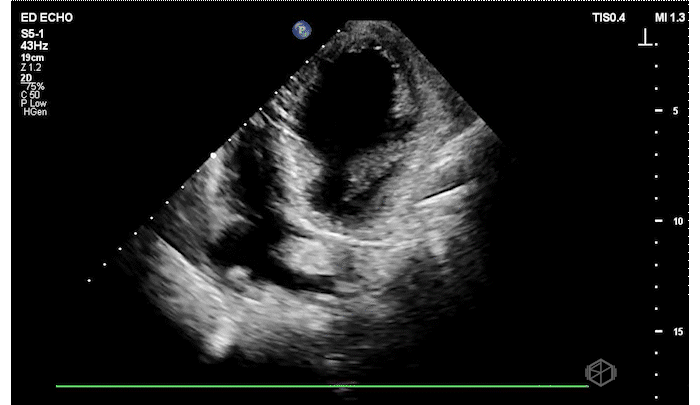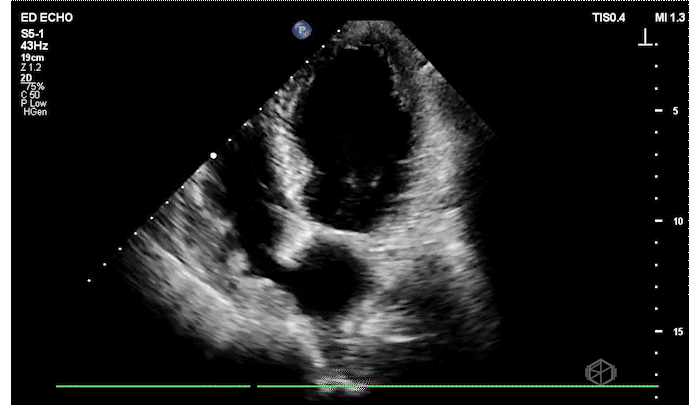
The patient has a significantly reduced LV systolic function. The AP4 view and the PSAX view both demonstrate extremely poor contractility. In the 3rd AP4 clip there is also a hyperechoic jelly like mass in the right atrium that is some what noticeable in the first clip, but more noticeable on the 3rd.
Diagnosis: Acute left ventricular systolic heart failure, right atrial hyperechoic mass
Learning points:
POCUS is a great tool to use to diagnose LV systolic heart failure early. It is one of the basic evaluations that is extremely useful. There are multiple times patient’s get told they have bronchitis, asthma, or some other diagnosis when they actually have heart failure.
LV systolic function can be evaluated using multiple methods.
Qualitative evaluation is the most commonly used method for POCUS. Qualitative evaluation improves with seeing and interpreting multiple echoes.
Emergency physicians are very good at visually determining normal LVSF and severely reduced LVSF. With mild or moderately reduced LVSF there is moderate agreement.
In order to qualitatively assess LVSF — look at how the overall left ventricle is moving: In PSAX and AP4, are the LV walls coming close to each other during systole? In parasternal long, Is the mitral valve almost touching the septum?
Quantitative evaluation of LV function is beyond the scope of most EM POCUS sonographers and may be covered at another time.
Regarding the right atrial mass — there are multiple diagnoses a right atrial mass could represent that require additional testing, from variant anatomy (remnant Eustachian valve) to thrombus or neoplasm. This patient had multiple additional tests including a cardiac MRI and TEE that could not differentiate between remnant Eustachian valve or thrombus so was started on anticoagulation.